Blood
Blood is a special type of fluid connective tissue derived from mesoderm.
The branch of science concerned with the study of blood, blood-forming tissues, and the disorders associated with them is called haematology.
haeme-blood and logos-study
PROPERTIES OF BLOOD
Colour : Bright red in arteries & dark red in veins
Mass : 8% of the body mass
pH : Slightly alkaline (pH = 7.35-7.45)
Taste : Salty
Temperature : 38° C (100.4° F)
Viscosity : 3-4 times more viscous than water
Volume : 5-6 litre
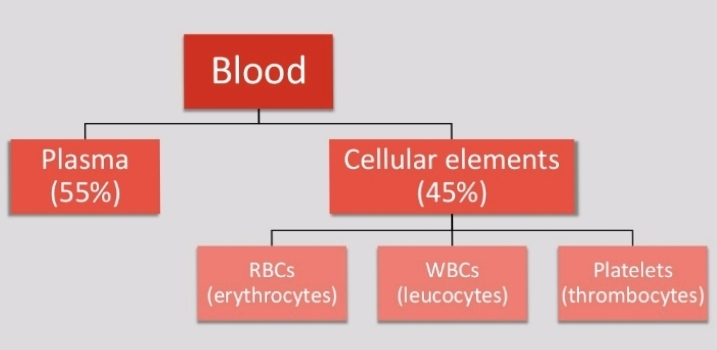
COMPOSITION OF BLOOD
Plasma
Plasma is a pale yellow coloured liquid component of a blood that holds the cellular elements of blood in suspension.
Constituents of plasma
Functions of plasma
Constituent. Function
Water. Absorbs, transports and releases heat
Albumins. Osmotic balance
Globulins. Defense mechanism
Fibrinogen. Blood clotting
Electrolytic ions. pH buffering
Red blood cells
Shape :- Circular biconcave non-nucleated
Size :- Diameter 7-8 μm Thickness 2.5 μm
Colour :- Red (haemoglobin pigment)
Count :- Adult male = 5.4 million RBCs/uL Adult female = 4.8 million RBCs/uL
Life Span :- 120 days
Erythropoiesis
The production of RBCs is known as erythropoiesis.
Adult :- Red bone marrow of long bones (hip bone, breast bone & ribs)
Child (upto 5 year) : Bone marrow of all the bones
Foetus : Liver & spleen
Increase in number of RBCS is known as polycythemia
Decrease in number of RBCs is known as erythropenia
Functions of RBCs
Transport O₂ from lungs to tissues
Transport CO₂ from tissues to lungs
Normal blood contains 13-15 g of Hb per 100 ml of blood
One RBC contains about 250 million molecules of Hb
Each molecule of Hb carries four molecules of oxygen
White blood cells
Shape : Amoeboid nucleated
Size : 12-15 μm
Colour : Colourless & translucent
Count : 5000-10000 WBCs/μL
Life span : 10-13 days
Leucopoiesis
The production of WBCS is known as leucopoiesis.
Adult :- Liver, spleen, tonsils, bone marrow
Foetus :- Liver, spleen
Increase in number of WBCS is known as leucocytosis
Decrease in number of WBCS is known as leucopenia Pathological increase in number of WBCS is known as leukemia (blood cancer)
Types of WBCs
Platelets
Shape :- Circular biconvex non-nucleated
Size :- 2-4 μm
Count :- 1,50,000 4,00,000 platelets/μL
Life span :- 5-9 days
Function :- Blood clotting
Thrombopoiesis
The production of platelets is known as thrombopoiesis.
Platelets are the fragments of large cells called megakaryocytes that remain in the bone marrow.
Increase in number of platelets is known as thrombocytosis
Decrease in number of platelets is known as thrombocytopenia
By : ummedsaini_


















No comments:
Post a Comment